360° Brain Static
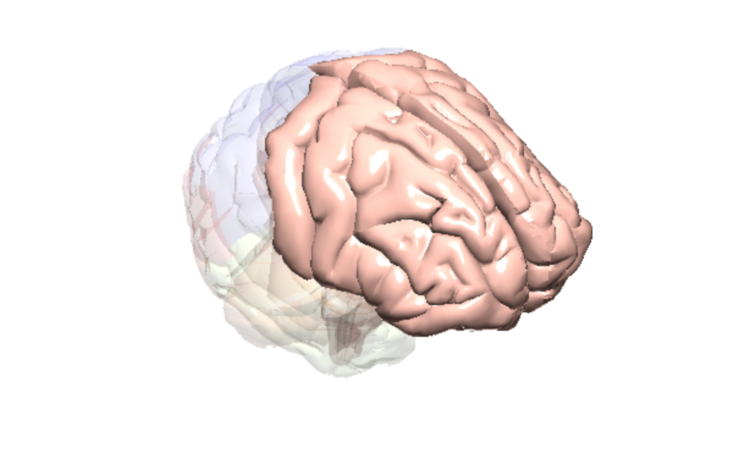
Frontal Lobe
Thinking & planning, decision making, senses, speech/language, behaviour.
Key Function
The frontal lobe is the area of the brain that plays a role in formation & retrieval of memories, problem solving, planning, language, speech, attention, and movement.
Fact
The compounds in cannabis (e.g., THC) bind to brain receptors (cannabinoid receptors) located in the frontal lobe. These compounds can change the way brain cells communicate with one another. In the frontal lobe, this can affect the way a person thinks, their ability to make decisions, plan and organize their thoughts and actions, create and retrieve memories, pay attention, speak and move.
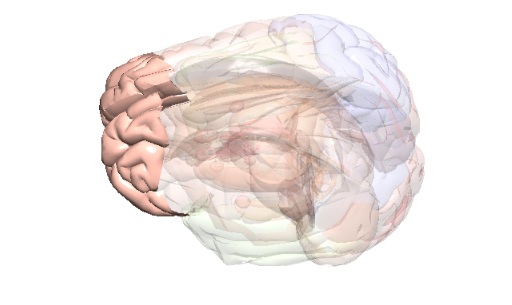
Prefrontal Cortex
Thinking & planning, decision making, behaviour.
Key Function
The prefrontal cortex is a part of the frontal lobe and is where the brain thinks, plans, and makes decisions.
Fact
The compounds in cannabis (e.g., THC) bind to brain receptors (cannabinoid receptors) located in the prefrontal cortex. These compounds can change the way brain cells communicate with one another. In the prefrontal cortex, this can affect the way a person thinks, their ability to make decisions, plan and organize their thoughts.
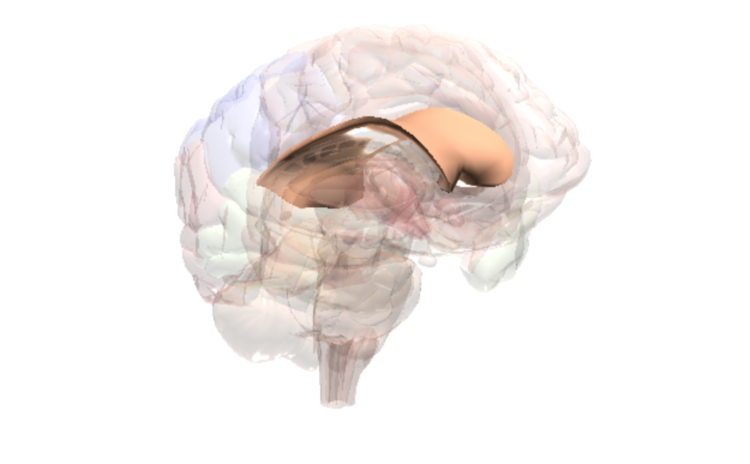
Corpus Callosum
Thinking & planning, movement & coordination, decision making, emotions and feelings, senses, behaviour.
Key Function
The corpus callosum connects the two hemispheres of the brain to help integrate information.
Fact
The compounds in cannabis (e.g., THC) bind to brain receptors (cannabinoid receptors) located in the corpus callosum. These compounds can change the way brain cells communicate with one another. In the corpus callosum, this can result in experiencing disorganized, strange or abnormal thoughts. This can also result in psychosis or schizophrenia (in those who are vulnerable).
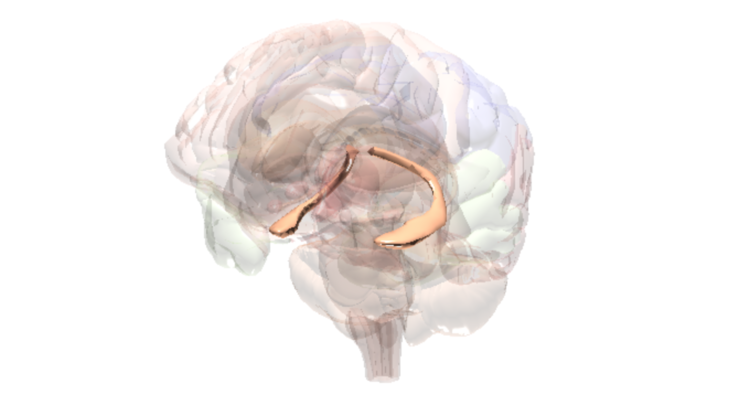
Hippocampus
Thinking & planning, decision making.
Key Function
The hippocampus is where the brain registers and stores memories.
Fact
The compounds in cannabis (e.g., THC) bind to brain receptors (cannabinoid receptors) located in the hippocampus. In the hippocampus, this can result in memory loss and difficulty learning new things and making decisions.
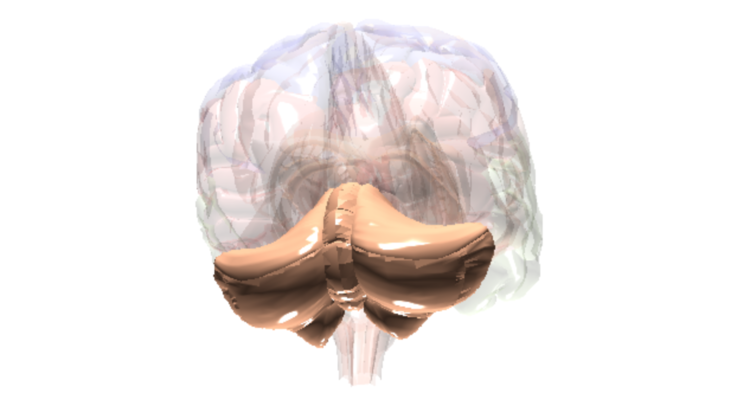
Cerebellum
Movement & Coordination
Key Function
The cerebellum is where the brain controls movement and coordination.
Fact
The compounds in cannabis (e.g., THC) bind to brain receptors (cannabinoid receptors) located in the cerebellum. These compounds can change the way brain cells communicate with one another. In the cerebellum, this can result in feelings of dizziness or a loss of balance/coordination which can make activities requiring coordination, such as driving, dangerous.

Basal Ganglia
Movement & Coordination
Key Function
The basal ganglia is where the brain controls movement and coordination.
Fact
The compounds in cannabis (e.g., THC) bind to brain receptors (cannabinoid receptors) located in the basal ganglia. These compounds can change the way brain cells communicate with one another. In the basal ganglia, this can result in problems with coordination which can make activities requiring coordination, such as driving, dangerous.
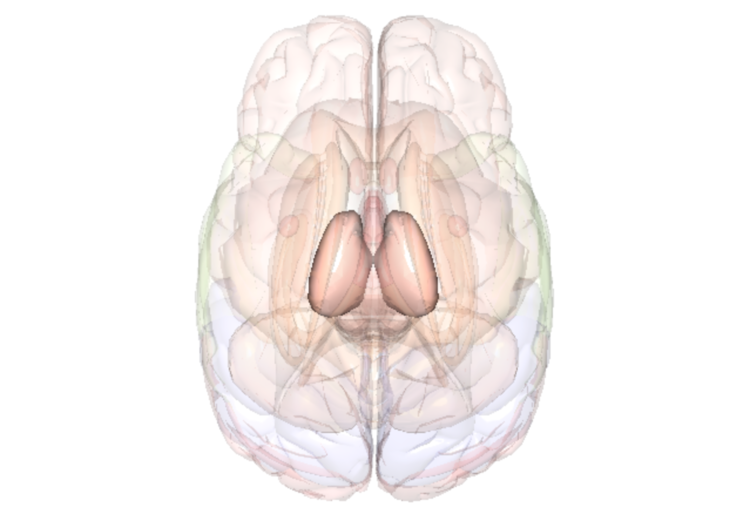
Thalamus
Movement & Coordination, Behaviour
Key Function
The thalamus is where the brain integrates and helps make sense of information such as sensory information coming from many other brain areas. The thalamus also plays a role in sleep/wakefulness, mood and behaviour including movement. The thalamus may also play a role in psychosis/schizophrenia.
Fact
The compounds in cannabis (e.g., THC) bind to brain receptors (cannabinoid receptors) located in the thalamus. These compounds can change the way brain cells communicate with one another. In the thalamus, this can result in loss of coordination, changes in sleep/wake cycle, and changes in behaviour including psychosis or schizophrenia (in those who are vulnerable).

Orbitofrontal Cortex
Decision Making
Key Function
The orbitofrontal cortex is where the brain makes decisions.
Fact
The compounds in cannabis (e.g., THC) bind to brain receptors (cannabinoid receptors) located in the orbitofrontal cortex. These compounds can change the way brain cells communicate with one another. In the orbitofrontal cortex, this can affect one’s ability to make decisions.

Limbic System
Emotions And Feelings
Key Function
The limbic system is where the brain regulates emotions. It consists of the cingulate gyrus, the hippocampus and the amygdala.
Fact
The compounds in cannabis (e.g., THC) bind to brain receptors (cannabinoid receptors) located in the limbic system. These compounds can change the way brain cells communicate with one another. In the limbic system, this can result in changes in emotions such as feeling happy, excited, calm, or feeling anxious, depressed, or paranoid.
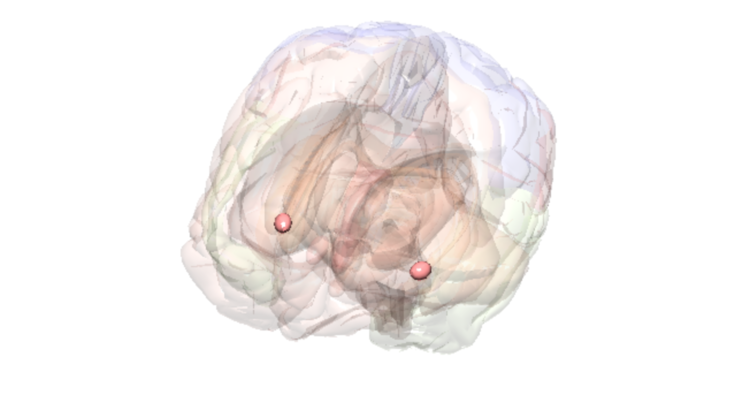
Amygdala
Emotions And Feelings
Key Function
The amygdala is where the brain processes emotions such as fear and anxiety.
Fact
The compounds in cannabis (e.g., THC) bind to brain receptors (cannabinoid receptors) located in the amygdala. These compounds can change the way brain cells communicate with one another. In the amygdala, this can result in changes in emotions such as feeling anxious, fearful or calm.

Hypothalamus
Emotions And Feelings, Behaviour
Key Function
The hypothalamus is where the brain controls sleep, motivation, appetite and thirst as well as response to stress.
Fact
The compounds in cannabis (e.g., THC) bind to brain receptors (cannabinoid receptors) located in the hypothalamus. These compounds can change the way brain cells communicate with one another. In the hypothalamus, this can result in feeling tired, sleepy and calm. This can also result in feeling hungry (‘the munchies’) and thirsty.

Nucleus Accumbens
Emotions And Feelings, Behaviour
Key Function
The nucleus accumbens is part of the brain’s pleasure and reward system and regulates motivation.
Fact
The compounds in cannabis (e.g., THC) bind to brain receptors (cannabinoid receptors) located in the nucleus accumbens. These compounds can change the way brain cells communicate with one another. In the nucleus accumbens, this can result in feeling ‘high’ when using cannabis and developing a dependence or addiction to cannabis.
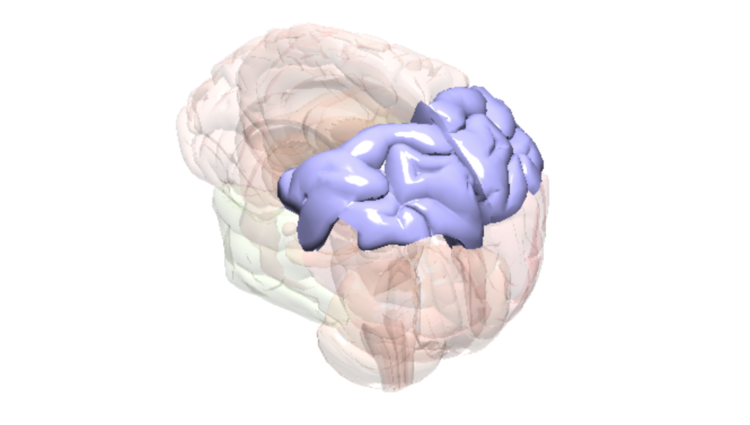
Parietal Lobe
Senses
Key Function
The parietal lobe is where the brain processes sensory information, helps to control movement and visual orientation, speech, visual perception and recognition.
Fact
The compounds in cannabis (e.g., THC) bind to brain receptors (cannabinoid receptors) located in the parietal lobe. These compounds can change the way brain cells communicate with one another. In the parietal lobe, this can result in altered sensations and perceptions including hallucinations, disorientation, confusion, loss of coordination, and problems speaking.

Occipital Lobe
Senses
Key Function
The occipital lobe is where the brain processes vision, spatial cues, and movement.
Fact
The compounds in cannabis (e.g., THC) bind to brain receptors (cannabinoid receptors) located in the occipital lobe. In the occipital lobe, this can result in changes in visual perception, ability to judge distances, and even hallucinations.

